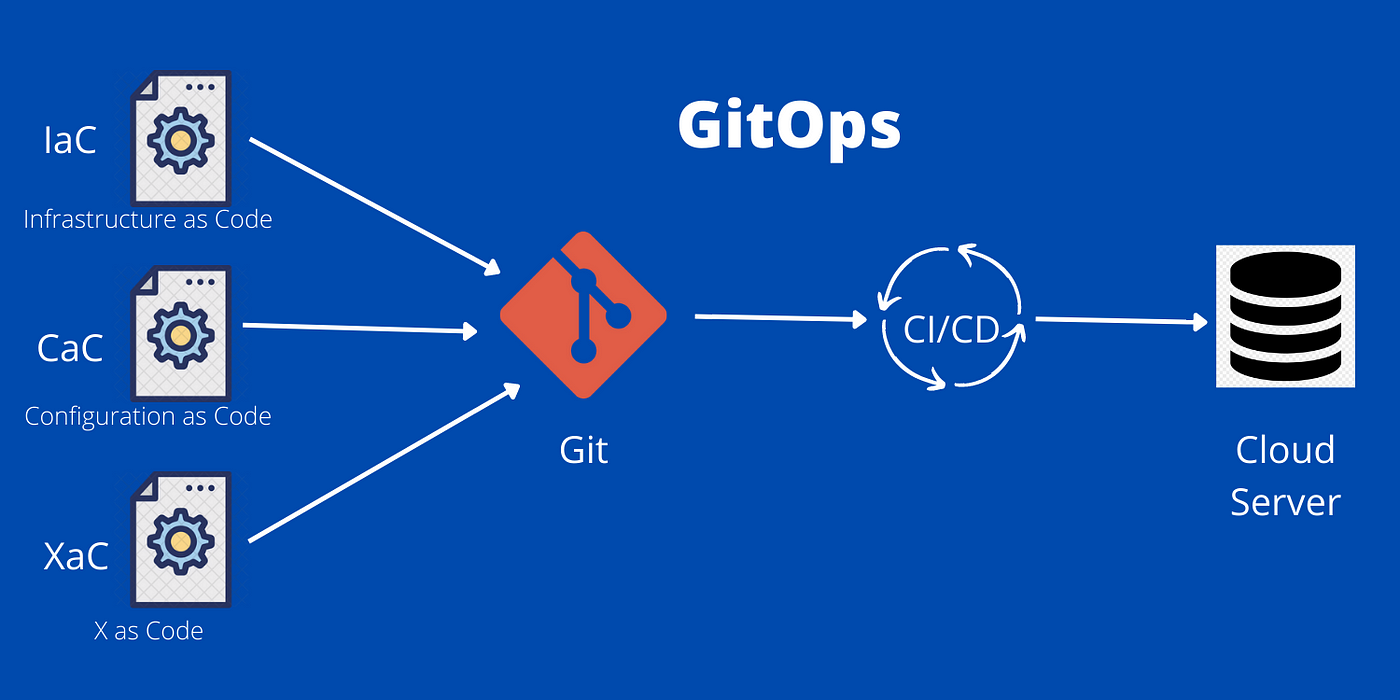
“Unleashing the Power of Speed: Revolutionizing Cloud and Edge Computing with 5G Technology”
The introduction about The Impact of 5G on Cloud Computing and Edge Computing:
The advent of 5G technology has brought about significant advancements in various industries, and cloud computing and edge computing are no exceptions. The combination of 5G and cloud computing has the potential to revolutionize the way data is processed, stored, and accessed. With faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, 5G enables seamless connectivity and opens up new possibilities for cloud computing and edge computing applications. This article explores the impact of 5G on these technologies, highlighting the benefits, challenges, and potential future developments.
The Advantages of 5G in Enhancing Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
The advent of 5G technology has brought about significant advancements in various industries, and one area that has greatly benefited from this is cloud computing and edge computing. The advantages of 5G in enhancing these computing technologies are numerous and have the potential to revolutionize the way we store, process, and access data.
One of the key advantages of 5G in cloud computing is its ability to provide faster and more reliable network connections. With 5G, data can be transmitted at incredibly high speeds, allowing for real-time access to cloud-based applications and services. This means that businesses can access their data and applications instantaneously, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Furthermore, 5G enables greater scalability in cloud computing. The increased bandwidth and lower latency of 5G networks allow for the seamless integration of more devices and applications into the cloud. This scalability is particularly beneficial for businesses that deal with large amounts of data or have a high demand for computing resources. With 5G, businesses can easily scale up or down their cloud infrastructure to meet their specific needs, without experiencing any performance issues.
In addition to enhancing cloud computing, 5G also has a significant impact on edge computing. Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to the source, rather than sending it to a centralized cloud server. This approach reduces latency and improves response times, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation.
5G technology enables edge computing by providing the necessary network capabilities. With 5G, data can be processed and analyzed at the edge of the network, closer to the devices generating the data. This reduces the need to transmit large amounts of data to a centralized cloud server, resulting in faster response times and reduced network congestion.
Moreover, 5G enables edge computing to be more efficient and cost-effective. By processing data locally, businesses can reduce their reliance on cloud resources, resulting in lower costs and improved resource allocation. This is particularly beneficial for applications that generate large amounts of data, as it reduces the need for expensive data storage and transmission.
Another advantage of 5G in edge computing is its ability to support mission-critical applications. With its ultra-low latency and high reliability, 5G networks are well-suited for applications that require real-time decision-making, such as remote surgery or emergency response systems. By enabling edge computing in these scenarios, 5G ensures that critical data is processed and acted upon immediately, potentially saving lives and improving outcomes.
In conclusion, the impact of 5G on cloud computing and edge computing is significant. The advantages of 5G in enhancing these computing technologies include faster and more reliable network connections, greater scalability, improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness, and support for mission-critical applications. As 5G continues to roll out globally, businesses and industries will undoubtedly benefit from the transformative capabilities it brings to cloud computing and edge computing.
The Role of 5G in Revolutionizing Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
The Role of 5G in Revolutionizing Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
In recent years, the world has witnessed a rapid advancement in technology, with 5G being at the forefront of this revolution. This fifth-generation wireless technology promises to bring about significant changes in various industries, and one area that stands to benefit greatly is cloud computing and edge computing.
Cloud computing has become an integral part of our daily lives, allowing us to store and access data and applications remotely. It has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing them with the flexibility and scalability they need to thrive in a fast-paced digital world. However, the current infrastructure supporting cloud computing is not without its limitations.
One of the main challenges faced by cloud computing is latency. Latency refers to the delay in data transmission between a user and the cloud server. This delay can be frustrating for users, especially in applications that require real-time data processing, such as online gaming or video streaming. With 5G, this latency issue can be significantly reduced, if not eliminated altogether.
5G offers ultra-low latency, with response times as low as one millisecond. This means that data can be transmitted and processed almost instantaneously, allowing for real-time interactions between users and cloud servers. This is a game-changer for cloud computing, as it opens up new possibilities for applications that require immediate data processing, such as autonomous vehicles or remote surgery.
Another area where 5G is set to revolutionize cloud computing is in the realm of edge computing. Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. This reduces the need for data to be transmitted back and forth between the cloud server and the user, resulting in faster response times and reduced network congestion.
With 5G, edge computing can reach its full potential. The high bandwidth and low latency offered by 5G enable edge devices to process and analyze data locally, without the need to rely heavily on the cloud server. This not only improves the performance of edge devices but also reduces the load on the cloud infrastructure, making it more efficient and cost-effective.
Furthermore, 5G allows for the seamless integration of cloud computing and edge computing. With its high-speed connectivity and low latency, 5G enables edge devices to offload computationally intensive tasks to the cloud server, while still maintaining real-time responsiveness. This hybrid approach combines the best of both worlds, leveraging the power of the cloud for complex computations and the agility of edge devices for real-time data processing.
The impact of 5G on cloud computing and edge computing goes beyond just improving performance and efficiency. It also opens up new opportunities for innovation and growth. With the ability to process and analyze data in real-time, businesses can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions faster than ever before. This can lead to the development of new products and services, as well as improved customer experiences.
In conclusion, 5G is set to revolutionize cloud computing and edge computing. Its ultra-low latency and high-speed connectivity will address the limitations of the current infrastructure, enabling real-time data processing and reducing network congestion. This will not only improve the performance and efficiency of cloud computing and edge computing but also open up new opportunities for innovation and growth. As we embrace the era of 5G, the future of cloud computing and edge computing looks brighter than ever.
Exploring the Future of Cloud Computing and Edge Computing with 5G
The advent of 5G technology has brought about significant advancements in various industries, and cloud computing and edge computing are no exceptions. As we explore the future of these computing paradigms with the integration of 5G, it becomes evident that they will undergo transformative changes, enabling faster and more efficient data processing.
Cloud computing, which involves the delivery of computing services over the internet, has revolutionized the way businesses operate. With the introduction of 5G, cloud computing is set to become even more powerful and accessible. The increased bandwidth and lower latency offered by 5G networks will allow for faster data transfer and processing, enabling businesses to leverage cloud computing capabilities more effectively.
One of the key benefits of 5G in cloud computing is its ability to handle massive amounts of data. With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the exponential growth of data generated by these devices, traditional cloud computing infrastructure may struggle to keep up. However, 5G networks can handle the massive influx of data, ensuring seamless connectivity and efficient data processing.
Moreover, 5G’s low latency capabilities will significantly enhance the performance of cloud computing. Latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. With 5G, latency is reduced to a minimum, enabling real-time data processing and analysis. This is particularly crucial for applications that require instant responses, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and augmented reality.
In addition to cloud computing, 5G also has a profound impact on edge computing. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing the need for data to travel back and forth to the cloud. With 5G, edge computing becomes even more efficient and reliable. The high-speed and low-latency capabilities of 5G networks enable faster data processing at the edge, reducing response times and improving overall performance.
The integration of 5G and edge computing is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time data analysis and decision-making. For example, in the context of smart cities, 5G-powered edge computing can enable real-time monitoring of traffic patterns, optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion. Similarly, in industrial settings, 5G and edge computing can facilitate real-time monitoring of machinery, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Furthermore, the combination of 5G, cloud computing, and edge computing opens up new possibilities for innovative applications. For instance, the healthcare industry can leverage this integration to enable remote patient monitoring and telemedicine services. With 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency, healthcare professionals can remotely monitor patients’ vital signs in real-time, providing timely interventions and improving patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the integration of 5G technology with cloud computing and edge computing has a profound impact on the future of these computing paradigms. The increased bandwidth, low latency, and real-time capabilities of 5G networks enable faster and more efficient data processing, revolutionizing industries such as healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing. As we continue to explore the potential of 5G, it is clear that it will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of cloud computing and edge computing.In conclusion, the deployment of 5G technology is expected to have a significant impact on both cloud computing and edge computing. With its high-speed and low-latency capabilities, 5G will enable faster data transfer and processing, making cloud computing more efficient and accessible. It will also facilitate the growth of edge computing by bringing computing resources closer to the data source, reducing latency and enabling real-time processing. Overall, the combination of 5G, cloud computing, and edge computing has the potential to revolutionize various industries and drive innovation in areas such as autonomous vehicles, IoT, and augmented reality.