Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of transportation, automotive software has emerged as a driving force behind the transformation of mobility. From advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) to autonomous vehicles, software technology is revolutionizing the way we move from point A to point B. In this article, we’ll delve into the pivotal role that automotive software plays in shaping the future of transportation.
Automotive software encompasses a wide range of applications and systems designed to enhance vehicle performance, safety, and connectivity. Traditionally, automobiles relied heavily on mechanical components, but the integration of software has led to a paradigm shift in the industry.
Definition
The design, development, production, marketing, and sales of motor vehicles are the activities of a vast array of businesses and organisations that make up the automotive industry. In terms of revenue, it is among the biggest industries worldwide. In terms of research and development spending, it is also the industry leader. NXP provides a wide range of automotive software tools that are intended to make the process of building ECUs based on NXP microcontrollers (MCU) easier and faster. This comprises a variety of drivers, libraries, stacks, and boot loader software in addition to run-time and embedded software and toolboxes compatible with MATLAB/Simulink. Additionally, NXP supports AUTOSAR microcontroller abstraction layers (MCAL) and operating systems (OS) by offering MCU initialization tools and auto code creation. Our committed team of experienced engineers can help you become more proficient by offering you customisation, development services, training, and advising on a variety of platforms and application areas.
Key Components of Automotive Software
Embedded Systems: These are specialized computing systems integrated into vehicles to control various functions such as engine management, braking, and climate control.
Infotainment Systems: Modern vehicles feature sophisticated infotainment systems that provide entertainment, navigation, and connectivity services to passengers.
Telematics: Telematics technology enables remote monitoring and communication with vehicles, facilitating features like GPS tracking, vehicle diagnostics, and remote control functionalities.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): ADAS utilize sensors, cameras, and software algorithms to enhance driver safety by providing features like adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and collision avoidance.
Autonomous Driving Software: At the forefront of automotive innovation, autonomous driving software enables vehicles to operate with varying degrees of autonomy, promising safer, more efficient transportation systems.
Impact of Automotive Software
Enhanced Safety: One of the most significant benefits of automotive software is its contribution to improved safety on the roads. ADAS features such as automatic emergency braking and blind-spot detection help prevent accidents and reduce the severity of collisions.
Efficiency and Sustainability: Software optimization of engine performance and vehicle systems leads to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, contributing to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Improved User Experience: Infotainment systems equipped with intuitive interfaces and connectivity options enhance the overall driving experience, keeping passengers entertained and informed while on the road.
Urban Mobility Solutions: With the rise of ride-sharing and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms, automotive software plays a crucial role in optimizing fleet management, route planning, and passenger experience in urban environments.
Paving the Way for Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous driving software holds the promise of revolutionizing transportation by eliminating human error, reducing traffic congestion, and enabling new mobility services such as robo-taxis and on-demand autonomous shuttles.
Challenges and Considerations
Cybersecurity: As vehicles become increasingly connected, cybersecurity emerges as a critical concern. Protecting automotive software systems from cyber threats is paramount to ensuring the safety and security of both vehicles and passengers.
Regulatory Compliance: The deployment of advanced automotive software, especially in autonomous vehicles, raises complex regulatory challenges related to safety standards, liability, and ethical considerations.
Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility and interoperability between different automotive software systems is essential for seamless integration and interoperability across vehicles and infrastructure.
Future Directions
Continued Innovation: The rapid pace of technological advancement in automotive software is expected to continue, with ongoing developments in areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technology.
Convergence of Industries: Automotive software is blurring the lines between traditional automotive OEMs and technology companies, leading to increased collaboration and convergence across industries.
Sustainable Mobility: As the world shifts towards sustainable transportation solutions, automotive software will play a pivotal role in enabling electric and autonomous vehicles, as well as supporting alternative mobility models such as car-sharing and micro-mobility.
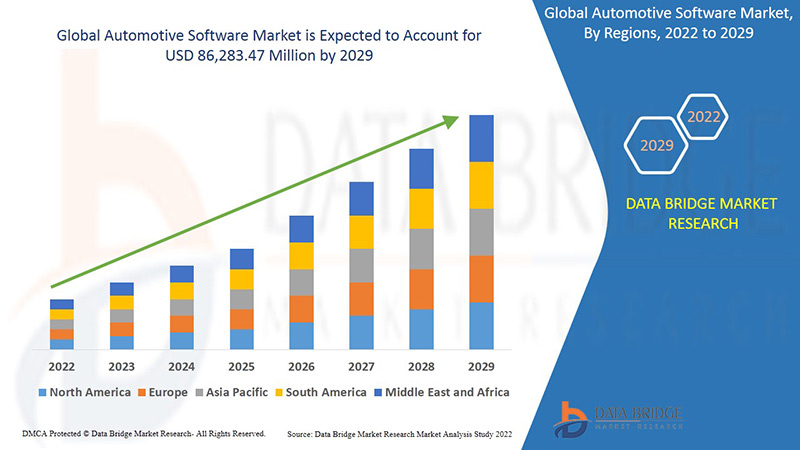
Growth Rate of Automotive Software Market
According to Data Bridge industry Research’s analysis, the automotive software industry is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 17.7% to reach a valuation of USD 86,283.47 million by 2029.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-automotive-software-market
Conclusion
Automotive software is at the forefront of revolutionizing mobility, driving innovation in vehicle safety, efficiency, and user experience. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the role of automotive software in shaping the future of transportation. By addressing challenges and embracing opportunities, stakeholders in the automotive industry can harness the power of software to create safer, more sustainable, and more connected mobility solutions for the future.