Wounds are a common occurrence in everyday life, ranging from minor cuts and scrapes to more severe injuries. Proper wound treatment is crucial not only for alleviating pain and discomfort but also for preventing complications such as infection and scarring. Chronic Wound Treatment In Dubai encompasses a range of techniques and strategies aimed at promoting healing and preventing complications. Whether it’s a small cut or a major surgical incision, timely and appropriate care can make a significant difference in the outcome. In this article A Comprehensive Guide to Treating Wounds guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about treating wounds effectively.
Understanding Different Types of Wounds
-
Traumatic Wounds
Traumatic wounds are caused by external forces such as cuts, abrasions, and punctures. These injuries often result from accidents or injuries sustained during physical activity.
-
Surgical Wounds
Surgical wounds are incisions made during surgical procedures. Proper care of surgical wounds is essential to prevent infection and promote optimal healing.
-
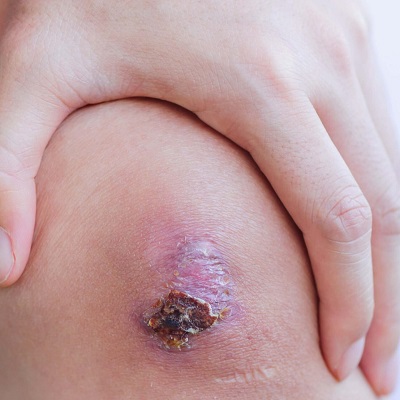
Chronic Wounds
Chronic wounds are those that fail to heal within a reasonable amount of time, often due to underlying health conditions such as diabetes or poor circulation. These wounds require specialized treatment to facilitate healing.
Initial Steps in Wound Care
-
Assessment of Wound Severity
The first step in treating a wound is to assess its severity. This involves evaluating factors such as the size, depth, and location of the wound, as well as the presence of any foreign objects or debris.
-
Cleaning and Disinfecting
Once the wound has been assessed, it should be cleaned and disinfected to remove any dirt, bacteria, or other contaminants. This helps reduce the risk of infection and promotes healing.
-
Applying Dressings
After cleaning the wound, it should be covered with an appropriate dressing to protect it from further injury and promote a moist healing environment. The type of dressing used will depend on the nature of the wound and the stage of healing.
Advanced Wound Care Techniques
-
Debridement
Debridement is the process of removing dead or damaged tissue from a wound to promote healing. This can be done through surgical, mechanical, enzymatic, or biological means.
-
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is a non-invasive technique that uses negative pressure to promote wound healing. It helps remove excess fluid, reduce swelling, and stimulate blood flow to the wound area.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves exposing the body to high levels of oxygen in a pressurized chamber. This helps increase oxygen delivery to the tissues, which can accelerate healing and reduce the risk of infection.
Managing Wound Healing
-
Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for supporting the body’s healing processes. Adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and protein can help promote tissue repair and regeneration.
-
Preventing Infection
Preventing infection is crucial for successful wound healing. This includes keeping the wound clean and dry, avoiding exposure to contaminants, and following appropriate hygiene practices.
-
Monitoring Progress
Regular monitoring of the wound is necessary to assess healing progress and identify any signs of complications. This may involve measuring wound size, evaluating tissue color and texture, and monitoring for signs of infection.
Special Considerations for Specific Wound Types
-
Burns
Burn wounds require specialized care to prevent infection and promote healing. This may include cleaning the wound, applying topical ointments, and protecting the area from further injury.
-
Pressure Ulcers
Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, are caused by prolonged pressure on the skin. Treatment typically involves relieving pressure on the affected area, keeping the wound clean and dry, and promoting circulation.
-
Diabetic Ulcers
Diabetic ulcers are a common complication of diabetes and require careful management to prevent infection and promote healing. This may include controlling blood sugar levels, keeping the wound clean, and using specialized dressings.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
-
Herbal Remedies
Some herbal remedies have been used for centuries to treat wounds and promote healing. Examples include aloe vera, calendula, and comfrey.
-
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese therapy that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to promote healing and relieve pain. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help accelerate wound healing.
-
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a technique that teaches individuals to control physiological processes such as heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension. It may be used as a complementary therapy to promote relaxation and reduce stress, which can aid in wound healing.
Rehabilitation and Follow-Up Care
-
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy may be recommended to help restore function and mobility following a severe wound or injury. This may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
-
Emotional Support
Dealing with a wound can be emotionally challenging, especially if it affects daily activities or quality of life. Emotional support from friends, family, or mental health professionals can play a crucial role in the healing process.
-
Preventing Recurrence
Once a wound has healed, it’s essential to take steps to prevent recurrence. This may involve lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and practicing good hygiene.
The Role of Medical Professionals in Wound Treatment
-
Doctors
Physicians play a central role in diagnosing and treating wounds, especially those that are severe or complicated. They may prescribe medications, perform procedures, or refer patients to specialists for further care.
-
Nurses
Nurses are often responsible for providing hands-on wound care, including cleaning, dressing changes, and monitoring for signs of infection. They also educate patients and caregivers about proper wound care techniques.
-
Wound Care Specialists
Chronic Wounds Treatment care specialists are healthcare professionals with specialized training in managing complex or non-healing wounds. They may work in hospitals, clinics, or specialized wound care centers.
Conclusion
Effective wound treatment requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the unique needs of each patient. By understanding A Comprehensive Guide to Treating Wounds different types of wounds, implementing appropriate care techniques, and involving medical professionals as needed, individuals can promote optimal healing and reduce the risk of complications.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How long does it take for a wound to heal?
The healing time for a wound depends on various factors, including its size, depth, and location, as well as the individual’s overall health and immune function. Minor wounds may heal within a few days to a week, while more severe or chronic wounds may take several weeks or months to heal completely.
2. What are the signs of infection in a wound?
Signs of infection in a wound may include increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, and drainage of pus. Fever, chills, and fatigue may also indicate an infection.
3. When should I seek medical attention for a wound?
It’s essential to seek medical attention for deep wounds, gaping, or won’t stop bleeding, as well as those that show signs of infection or are slow to heal. Additionally, individuals with underlying health conditions such as diabetes or compromised immune systems should consult a healthcare professional for guidance on wound care.
4. Can I treat a wound at home, or do I need to see a doctor?
Minor wounds can often be treated at home with proper cleaning and dressing. However, it’s essential to seek medical attention for wounds that are severe, infected, or fail to improve with home care. A healthcare professional can assess the wound and recommend appropriate treatment.
5. How can I prevent scars from forming after a wound heals?
To minimize scarring, it’s essential to keep the wound clean and moist during the healing process. Avoid picking at scabs or applying harsh chemicals to the area. If necessary, consult a dermatologist for advice on scar management techniques.